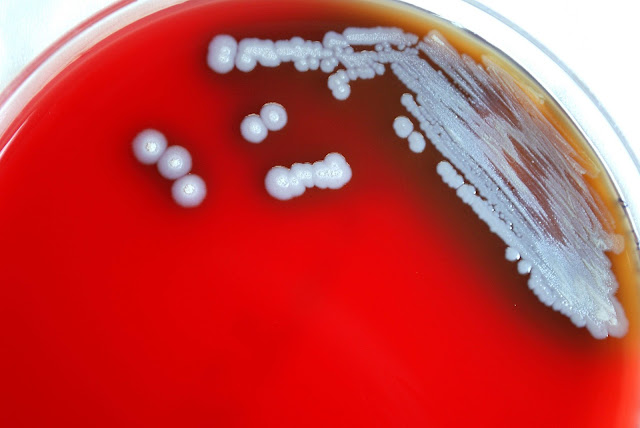
The Rising Burden of Burkholderia Infections: What You Need to Know
 |
| Burkholderia Infections |
A genus of Gram-negative bacteria
called Burkholderia may be found in soil, water, and plants. While certain
species are known to be unharmful, others are known to infect people,
especially those with compromised immune systems. It can be challenging to detect
and treat Burkholderia infections, which can vary from minor skin infections to
fatal systemic infections.
Melioidosis, which is brought on
by Burkholderia pseudomallei, is one of the most well-known Burkholderia
infections. Although it has been documented in various regions of the
world, melioidosis is most common in Southeast Asia and Northern Australia.
Through cuts, wounds, inhalation, or consumption of polluted water or soil, the
bacteria can enter the body. Melioidosis can cause a wide range of symptoms,
from organ failure and respiratory distress to fever and muscular pains. If the
illness is not identified and treated right away, it might be deadly.
Burkholderia cepacia complex
(BCC) infection is a different Burkholderia infection that has attracted
interest lately. BCC is a genus of bacteria that can infect persons with
compromised immune systems or persistent lung conditions like cystic fibrosis.
They are typically found in soil and water. A BCC infection can result in
bloodstream infections, sepsis, and respiratory symptoms as coughing, wheezing,
and shortness of breath.
Burkholderia infections can be
difficult to diagnose because the bacteria can be tricky to cultivate in a lab
and because their symptoms might be mistaken for those of other illnesses.
Although laboratory procedures like blood cultures and molecular assays may not
be widely accessible in all healthcare settings, they can assist identify the
bacterium. Antibiotic resistance can also make it more difficult to treat
Burkholderia infections since some strains of the bacterium have become
resistant to several different kinds of antibiotics.
Burkholderia infections are
routinely treated with a combination of antibiotics, frequently for a lengthy
period of time. For instance, the standard course of treatment for melioidosis
consists of several weeks of oral and intravenous antibiotic medication,
followed by long-term oral therapy. Treatment for BCC infections may combine
oral and inhaled antibiotics as well as additional supportive therapies
including oxygen therapy and chest physical therapy.
Burkholderia infections can be
difficult to prevent since the bacteria are so common in the environment.
However, taking precautions like caring for wounds properly, avoiding polluted
water and soil, and maintaining excellent hygiene can help lower the chance of
infection. Burkholderia infections can be stopped from spreading in hospital
settings by using infection control procedures including washing hands and
disinfecting equipment.


Comments
Post a Comment